tsconfig 옵션에 대해 알아보자.
by EarlyHail
tsconfig의 각 설정이 어디에 사용되는지 정리해보자.
모든 옵션에 대해 다루지 않으며, 세부적인 옵션은 typescript doc을 찾아보면 좋다.
기본 옵션들
{
"compilerOptions": {
"outDir": "dist",
"target": "es5",
"module": "commonjs",
"strict": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true
}
}
tsc --init명령어를 통해 tsconfig.json을 생성했을 때 설정되어 있는 기본 옵션들을 먼저 정리해보자.
outDir는 기본 옵션은 아니다.
outDir
compile 결과물의 출력 파일의 위치를 명시한다.
왼쪽 : "outDir": "dist" / 오른쪽 : 설정X
target
target ECMAscript 버전을 명시해준다.
해당 버전으로 transpiling된 코드가 출력된다.
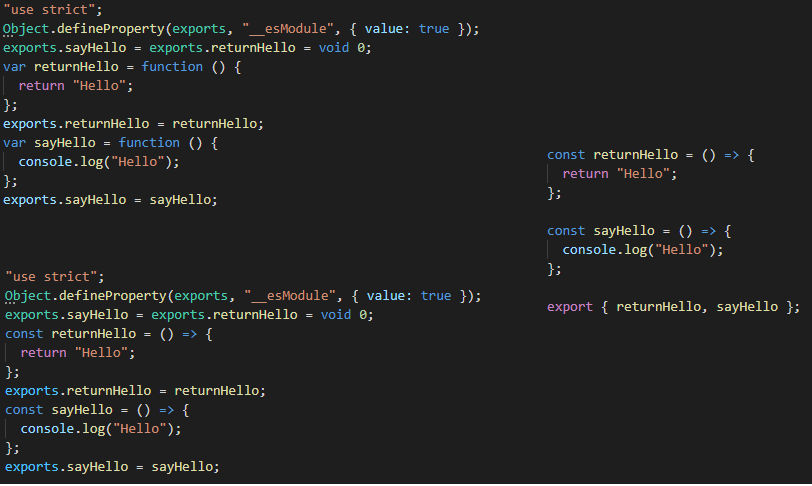
왼쪽 위 : "target": "es5" / 왼쪽 아래 : "target": "es6" / 오른쪽 : 원본
module
모듈 호출 방법을 설정해준다.
-
원본
-
export
const returnHello = () => { return "Hello"; }; const sayHello = () => { console.log("Hello"); }; export { returnHello, sayHello }; -
import
import { sayHello, returnHello } from "./hello/hello"; sayHello(); console.log(returnHello());
-
-
es6
-
export
var returnHello = function () { return "Hello"; }; var sayHello = function () { console.log("Hello"); }; export { returnHello, sayHello }; -
import
import { sayHello, returnHello } from "./hello/hello"; sayHello(); console.log(returnHello());
-
-
commonjs
-
export
"use strict"; Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true }); exports.sayHello = exports.returnHello = void 0; var returnHello = function () { return "Hello"; }; exports.returnHello = returnHello; var sayHello = function () { console.log("Hello"); }; exports.sayHello = sayHello; -
import
"use strict"; Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true }); const hello_1 = require("./hello/hello"); hello_1.sayHello(); console.log(hello_1.returnHello());
-
strict
모든 strict 타입 검사 옵션을 활성화 시킨다.
-
타입 검사 항목
-
noImplicitAny
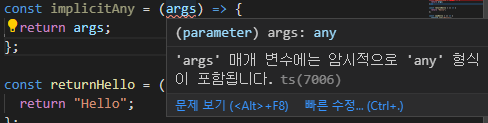
noImplicitAny: true일 경우 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
-
noImplicitThis
const obj = { num: 10, getNumFunc: function () { return function () { return this.num; }; }, };위 상황에서
this는 암시적 바인딩에 의해 상황에 따라 바뀔 수 있다.global에서 선언할 경우 window, this가 바인딩 된 상태에서 호출될 경우 해당 객체의 this를 가르킨다.
const obj = { num: 10, getNumFunc: function () { return function () { return this.num; }; }, }; const obj2 = { num: 20, func: obj.getNumFunc(), }; obj2.func(); // 출력 : 20따라서 암시적인 this의 any타입을 허용해 주거나, arrow 함수로 선언하여 this가
obj임을 명확하게 해주어야 한다. -
alwaysStrict
각 소스파일에
"use strict"를 추가한다. -
strictNullChecks
const a: null = null; const b: number = a;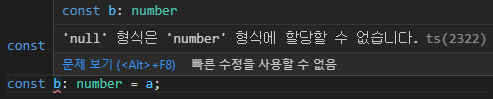
-
strictFunctionTypes
bivariant parameter check를 허용하지 않는다.
class A { private name: string; constructor() { this.name = "a"; } } class B extends A {} class C extends B {} class D {} const func = (param: A) => { return param; }; const a = new A(); const b = new B(); const c = new C(); const d = new D(); func(a); func(b); func(c); func(d);
A의 구현체가 없으면 에러가 발생하지 않는다!!!
-
esModuleInterop
런타임 바벨 호환성을 위해 __importStar와 __importDefault를 추가해준다고 하는데…. 잘 모르겠다.
skipLibCheck
모든 type definition 파일 (*.d.ts)의 검사를 하지 않는다. 라고 하는데… true로 놔도 열심히 검사한다.
type의 정확도를 검사하는 비용을 줄이기 위해서 사용된다.
tsconfig doc에는 사용한 소스코드에 대해서만 타입체크를 진행한다 라고 써져있는데 false로 설정해도 사용하지 않은 라이브러리에 대해서는 타입체크를 하지 않는다.
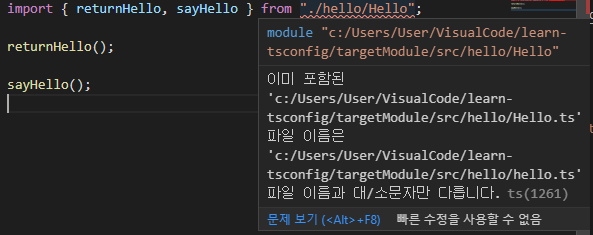
forceConsistentCasingInFileNames
모듈을 import할 때 실제 파일 이름과 casing이 동일해야 함을 명시한다.
import { returnHello, sayHello } from "./hello/Hello"; //실제 파일 이름은 hello.ts
returnHello();
sayHello();