call, apply, bind에 대해 알아보자 (feat. this)
by EarlyHail
어디서 한번쯤은 봤지만 뭔지 정확히 모르는 함수, call, apply, bind에 대해 알아보자
call과 apply
call과 apply는 함수를 호출하는 방법이다.
const whatThis = function (a, b) {
console.log(this);
};
whatThis(); // this: Window, a: undefined, b: undefined
whatThis.call({ greet: "안녕" }, 1, 2); // this: { greet: "안녕" }, a: 1, b: 2
whatThis.call({ greet: "안녕" }, [1, 2]); // this: { greet: "안녕" }, a: [1, 2], b: undefined
whatThis.apply({ greet: "안녕" }, 1, 2); // Uncaught TypeError: CreateListFromArrayLike called on non-object
whatThis.apply({ greet: "안녕" }, [1, 2]); // this: { greet: "안녕" }, a: 1, b: 2
-
call은 인자를 각각 전달한다.
-
apply는 인자를
배열로 전달한다. (두 번째 인자는 배열이어야 한다)
call의 사용 예시
-
call과 apply는 이미 할당되어 있는 다른 객체의 함수를 해당 객체에 재할당할 때 사용한다.
function Product(name, price) { this.name = name; this.price = price; if (price < 0) { throw RangeError( "Cannot create product " + this.name + " with a negative price" ); } } function Food(name, price) { // Product(this, name, price); Product.call(this, name, price); this.category = "food"; } function Toy(name, price) { // Product(this, name, price); Product.call(this, name, price); this.category = "toy"; } const cheese = new Food("feta", 5); console.log(cheese); const fun = new Toy("robot", 40); console.log(fun);-
일반 Product 호출

-
call로 this를 바인딩 하여 Product 호출
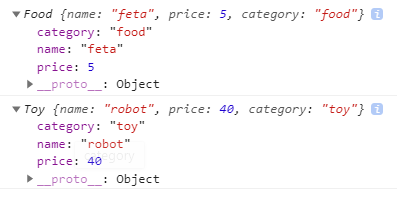
-
apply의 사용 예시
-
apply로 원본 배열에 새로운 배열을 이어서 붙일 수 있다.
concat 함수가 존재 하지만, concat은 새로운 배열을 반환한다.
const a = [1, 2, 3]; const b = [4, 5]; a.push.apply(a, b); console.log(a); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] const numbers = [8, 7, 5, 2, 4]; console.log(Math.max.apply(null, numbers)); Array.prototype.max = function () { return Math.max.apply(null, this); }; console.log(numbers.max());-
push
a.push를 하게 되면 push는 자신을 호출한 a를this로 참조할 것이기 때문에 apply의 this를a로,b를 안자로 넘겨서 만들 수 있다.사실
spread operator를 사용하면 더 직관적이고 간결하게 구현할 수 있다.const a = [1, 2, 3]; const b = [4, 5]; a.push(...b); console.log(a); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] -
max
Math.max같은 경우 일부 내장함수 같은 경우 위 예시처럼 루프 없이 각 원소에 대해 함수를 적용하도록 만들어 준다고 하는데Math.max가 어떻게 구현되어 있는지 모르는 상태에서 위 코드를 사용하는건 매우 지양해야 할것 같다.
-
bind
call과 apply가 this를 설정하면서 실행까지 해준다면, bind는 this만 설정 해준다.
const module = {
x: 41,
getX: function () {
console.log(this);
return this.x;
},
};
console.log(module.getX()); // this가 module이므로 41
const getX = module.getX;
console.log(getX()); // this가 window이므로 undefined
const bindedGetX = getX.bind(module);
console.log(bindedGetX()); // this가 module이므로 41
정리
bind - 함수의 this를 설정
call - 함수의 this를 설정, 인자를 받아서 함수를 실행
apply - 함수의 this를 설정, 인자를 하나의 배열로 받아서 함수를 실행
Reference