Composite 패턴
by EarlyHail
Composite
부분과 전체의 계층을 표현하기 위해 객체들을 모아 트리구조로 구성한다. 사용자로 하여금 개별 객체와 복합 객체를 모두 동일하게 다룰 수 있도록 하는 패턴이다.
-
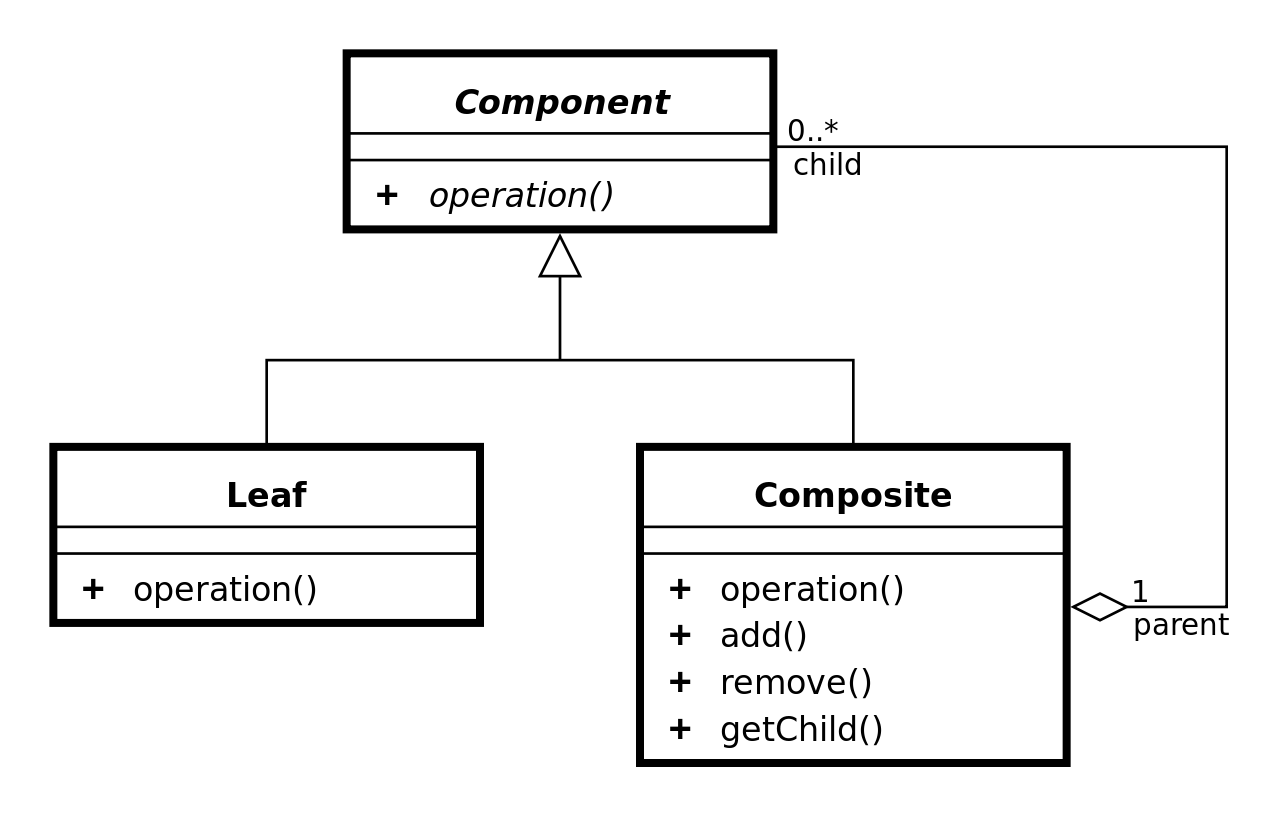
Component
집합 관계에 정의될 모든 객체에 대한 인터페이스를 정의한다.
모든 클래스에 해당하는 인터페이스에 대해서는 공통의 행동을 구현한다.
전체 클래스에 속한 요소들을 관리하는데 필요한 인터페이스를 정의한다.
순환 구조에서 요소들을 포함하는 전체 클래스로 접근하는데 필요한 인터페이스를 정의하며 경우에 따라 인터페이스를 구현한다.
-
Leaf
가장 말단의 객체, 즉 자식이 없는 객체를 나타낸다.
객체 합성에 가장 기본이 되는 객체의 행동을 정의한다.
-
Composite
자식이 있는 구성요소에 대한 행동을 정의한다.
자신이 Composite하는 요소들을 저장하면서
Component인터페이스에 정의된 자식 관련 연산을 구현한다.
Composite 패턴 적용
-
Component
abstract class Equipment { constructor( protected equipmentPower: number, protected equipmentPrice: number ) {} abstract power(): number; abstract price(): number; }전체 클래스에 속한 요소들을 관리하는데 필요한 인터페이스는 정의하지 않았다.
- Component에 있을 필요가 없어 보였다.
- Leaf는 자신의 할 일만 하면 되므로 관리가 필요 없기 때문에
Component보다는Composite에 있는게 자연스럽다고 생각했다.
-
Leaf
class PCComponent extends Equipment { power(): number { return this.equipmentPower; } price(): number { return this.equipmentPrice; } } -
Composite
class CompositeEquipment extends Equipment { private equipments: Equipment[] = []; power(): number { return ( this.equipmentPower + this.equipments.reduce((acc: number, cur: Equipment): number => { return acc + cur.power(); }, 0) ); } price(): number { return ( this.equipmentPrice + this.equipments.reduce((acc: number, cur: Equipment): number => { return acc + cur.price(); }, 0) ); } add(equipment: Equipment): void { this.equipments.push(equipment); } remove(equipment: Equipment): void { this.equipments = this.equipments.filter( (currentEquipment) => currentEquipment != equipment ); } } -
사용
const cpu = new PCComponent(100, 200000); const ram = new PCComponent(5, 80000); const motherboard = new CompositeEquipment(20, 100000); const pcCase = new CompositeEquipment(30, 50000); pcCase.add(motherboard); motherboard.add(cpu); motherboard.add(ram); console.log(motherboard.price()); console.log(motherboard.power()); console.log(pcCase.price()); console.log(pcCase.power());
Composite Pattern은 구현 의도에 따라서 많이 달라질 가능성이 있는것 같다.
내가 한것 처럼 전체 클래스에 속한 요소들을 관리하는데 필요한 인터페이스를 Component가 아닌 실제 사용하는 Composite에 구현할 수도 있을것 같고
Leaf에 구현해야할 객체 합성에 가장 기본이 되는 행동을 Component에 정의해 두고, Composite는 메소드 오버라이딩을 통해 구현하는 방법도 고려해볼만한 방법인것 같았다.